
检验医学 ›› 2022, Vol. 37 ›› Issue (8): 710-714.DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8640.2022.08.002
赵旭亮1, 田瑞霞2, 李旭3, 贾建安4, 俞敏2, 朱复希1( )
)
收稿日期:2021-02-25
修回日期:2022-05-18
出版日期:2022-08-30
发布日期:2022-09-16
通讯作者:
朱复希
作者简介:朱复希,E-mail: fxzhu@163.com。基金资助:
ZHAO Xuliang1, TIAN Ruixia2, LI Xu3, JIA Jian'an4, YU Min2, ZHU Fuxi1( )
)
Received:2021-02-25
Revised:2022-05-18
Online:2022-08-30
Published:2022-09-16
Contact:
ZHU Fuxi
摘要:
目的 对1例耳-腭-指综合征1型(OPD1)患儿围产期的临床特征和遗传特点进行分析,提高临床对此类罕见病的认识。方法 收集1例OPD1患儿的临床资料,对患儿及其父母进行全外显子家系测序(Trio-WES)。采用Sanger测序对变异位点进行验证。采用生物信息学分析评估变异位点的危害性。结合文献对细丝蛋白A(FLNA)基因热点变异患儿的临床特征进行回顾性分析。结果 产前超声提示患儿小下颌、鼻梁塌陷、脊椎排列异常、双足第2趾长,出生后患儿具有眼距较宽、眼睑裂倾斜、鼻梁塌陷、下颌后缩、耳位低且右耳可见副耳、双足第2趾明显长于其余4趾的体貌特征。基因检测结果提示患儿FLNA基因发生杂合变异(c.620C>T/p.Pro207Leu),患儿母亲存在该位点变异,父亲基因型为野生型。文献回顾分析结果显示,FLNA基因c.620C>T/p.Pro207Leu是导致OPD1的热点变异,携带该变异的患者可表现为眼距宽、眼睑裂倾斜、小下颌、腭裂、不同类型的指(趾)骨畸形、听力下降等临床特征。结论 FLNA基因c.620C>T/p.Pro207Leu变异可导致OPD1的发生。结合家系资料分析、产前超声检查和家系基因分析是诊断耳-腭-指谱系障碍(OPDSD)并进一步分型的有效方法。
中图分类号:
赵旭亮, 田瑞霞, 李旭, 贾建安, 俞敏, 朱复希. 耳-腭-指综合征1型新生儿围产期临床特征和遗传特点分析[J]. 检验医学, 2022, 37(8): 710-714.
ZHAO Xuliang, TIAN Ruixia, LI Xu, JIA Jian'an, YU Min, ZHU Fuxi. Analysis of perinatal clinical features and genetic characteristics of a neonate with otopalatodigital syndrome type 1[J]. Laboratory Medicine, 2022, 37(8): 710-714.
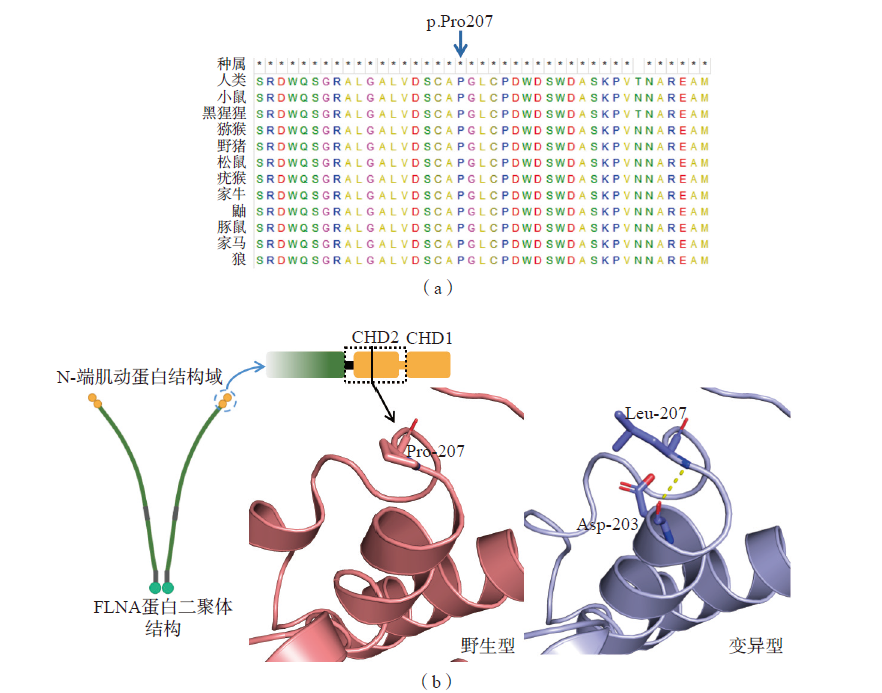
图4 FLNA基因c.620C>T/p.Pro207Leu变异位点危害性分析 注:(a)FLNA蛋白第207号脯氨酸在不同物种间高度保守(蓝色箭头);(b)FLNA蛋白二聚体结构简图,N-端肌动蛋白结合域由钙调节蛋白同源结构域(calponin homology domain,CHD)1及CHD2组成,可与F-肌动蛋白结合,并具有信号转导功能;本例患儿变异位点c.620C>T/p.Pro207Leu位于CHD2区域,可与第203号天冬氨酸(Asp-203)残基形成氢键,进而对结构稳定性产生局部影响。
| 病例 | 性别 | 确诊时间 | 眼距较宽 | 眼睑裂倾斜 | 鼻梁塌 | 低耳位 | 小下颌 | 腭裂 | 指(趾)骨畸形 | 脊椎侧弯 | 听力下降 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 本例患儿 | 男 | 出生1 d | + | + | + | + | + | - | + | + | |
| 病例1[ | 男 | 孕36周 | + | + | + | + | + | - | + | - | |
| 病例2[ | 男 | 孕22周 | + | + | + | + | + | - | + | + | |
| 病例3[ | 男 | 6个月 | + | - | - | - | - | - | + | - | + |
| 病例4[ | 男 | 1个月 | + | + | - | - | - | + | + | - | + |
| 病例5[ | 男 | 11岁 | + | - | + | + | - | + | + | - | + |
| 病例6[ | 男 | 出生1 d | + | + | + | + | - | + | + | - | + |
表1 FLNA基因c.620C>T/p.Pro207Leu杂合变异患者及胎儿临床特征
| 病例 | 性别 | 确诊时间 | 眼距较宽 | 眼睑裂倾斜 | 鼻梁塌 | 低耳位 | 小下颌 | 腭裂 | 指(趾)骨畸形 | 脊椎侧弯 | 听力下降 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 本例患儿 | 男 | 出生1 d | + | + | + | + | + | - | + | + | |
| 病例1[ | 男 | 孕36周 | + | + | + | + | + | - | + | - | |
| 病例2[ | 男 | 孕22周 | + | + | + | + | + | - | + | + | |
| 病例3[ | 男 | 6个月 | + | - | - | - | - | - | + | - | + |
| 病例4[ | 男 | 1个月 | + | + | - | - | - | + | + | - | + |
| 病例5[ | 男 | 11岁 | + | - | + | + | - | + | + | - | + |
| 病例6[ | 男 | 出生1 d | + | + | + | + | - | + | + | - | + |
| [1] |
ROBERTSON S P. Otopalatodigital syndrome spectrum disorders:otopalatodigital syndrome types 1 and 2,frontometaphyseal dysplasia and melnick-needles syndrome[J]. Eur J Hum Genet, 2007, 15(1):3-9.
DOI URL |
| [2] | ROBERTSON S. X-linked otopalatodigital spectrum disorders[A]// ADAM M P, ARDINGER H H, PAGON R A, et al. Gene reviews[M]. Seattle: University of Washington,1993-2020. |
| [3] |
CANNAERTS E, SHUKLA A, HASANHODZIC M, et al. FLNA mutations in surviving males presenting with connective tissue findings:two new case reports and review of the literature[J]. BMC Med Genet, 2018, 19(1):140.
DOI URL |
| [4] | RICHARDS S, AZIZ N, BALE S, et al. Standards and guidelines for the interpretation of sequence variants:a joint consensus recommendation of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics and the Association for Molecular Pathology[J]. Genet Med, 2015, 17(5):405-424. |
| [5] | JOKSIC I, CUTURILO G, JURISIC A, et al. Otopalatodigital syndrome type Ⅰ:novel characteristics and prenatal manifestations in two siblings[J]. Balkan J Med Genet, 2019, 22(2):83-88. |
| [6] |
MOUTTON S, FERGELOT P, NAUDION S, et al. Otopalatodigital spectrum disorders:refinement of the phenotypic and mutational spectrum[J]. J Hum Genet, 2016, 61(8):693-699.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
ROBERTSON S P, THOMPSON S, MORGAN T, et al. Postzygotic mutation and germline mosaicism in the otopalatodigital syndrome spectrum disorders[J]. Eur J Hum Genet, 2006, 14(5):549-554.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
ROBERTSON S P, TWIGG S R, SUTHERLAND-SMITH A J, et al. Localized mutations in the gene encoding the cytoskeletal protein filamin A cause diverse malformations in humans[J]. Nat Genet, 2003, 33(4):487-491.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
NAKAMURA F, KUMETA K, HIDA T, et al. Amino- and carboxyl-terminal domains of filamin-A interact with CRMP1 to mediate Sema3A signalling[J]. Nat Commun, 2014, 5:5325.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
VERLOES A, LESENFANTS S, BARR M, et al. Fronto-otopalatodigital osteodysplasia:clinical evidence for a single entity encompassing melnick-needles syndrome,otopalatodigital syndrome types 1 and 2,and frontometaphyseal dysplasia[J]. Am J Med Genet, 2000, 90(5):407-422.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
GORLIN R J, COHEN M M Jr. Frontometaphyseal dysplasia. A new syndrome[J]. Am J Dis Child, 1969, 118(3):487-494.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
LEGGETT J M. Laryngo-tracheal stenosis in frontometaphyseal dysplasia[J]. J Laryngol Otol, 1988, 102(1):74-78.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
NAUDION S, MOUTTON S, COUPRY I, et al. Fetal phenotypes in otopalatodigital spectrum disorders[J]. Clin Genet, 2016, 89(3):371-377.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
MARIÑO-ENRÍQUEZ A, LAPUNZINA P, ROBERTSON S P, et al. Otopalatodigital syndrome type 2 in two siblings with a novel filamin A 629G>T mutation:clinical,pathological,and molecular findings[J]. Am J Med Genet A, 2007, 143A(10):1120-1125.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 范列英. 膜性肾病生物标志物的研究现状与应用展望[J]. 检验医学, 2023, 38(12): 1111-1114. |
| [2] | 孙林成, 李建锋, 程维丽, 姬攀云. 抗PLA2R IgG4抗体、PLA2R IgG4/IgG比值在原发性膜性肾病预后评估中的价值[J]. 检验医学, 2023, 38(12): 1115-1120. |
| [3] | 刘庆阳, 袁建明, 夏进军, 姜风英, 王秋波, 王晓明. 基于GEO数据库和临床样本验证CXCL9作为类风湿关节炎生物标志物的研究[J]. 检验医学, 2023, 38(12): 1121-1129. |
| [4] | 杨晓, 李恩灵, 吴丽霞, 戴颖欣, 王之青, 黄昊, 郑冰. 胞质型抗核抗体对间接免疫荧光法检测抗中性粒细胞胞质抗体的影响[J]. 检验医学, 2023, 38(12): 1135-1140. |
| [5] | 项瑾, 刘爱平, 胡尧, 吴之源, 曹国君, 关明. 新型冠状病毒肺炎患者抗核抗体谱分析和血清加热灭活对检测的影响[J]. 检验医学, 2023, 38(12): 1141-1146. |
| [6] | 成宇, 徐臻, 陆柳, 丁梦蕾, 虞珊珊, 宗明, 范列英. 新型冠状病毒肺炎患者血清抗ACE-2抗体表达及其影响因素分析[J]. 检验医学, 2023, 38(12): 1147-1152. |
| [7] | 游延军, 张欢, 向乾银, 曹长春, 王健, 曾红, 魏元敏, 吴斌, 黄敬双, 季纯宇, 代苗, 秦枫. 原发性膜性肾病标志物抗PLA2R抗体检测方法比较[J]. 检验医学, 2023, 38(12): 1153-1156. |
| [8] | 王丽, 陈琳, 黄卓春. 易误判的ANA荧光模型1例报道[J]. 检验医学, 2023, 38(12): 1157-1159. |
| [9] | 王洪玲, 刘梦娜, 白萍, 廖焕金. AML患者异基因造血干细胞移植后复发危险因素分析[J]. 检验医学, 2023, 38(12): 1160-1166. |
| [10] | 杨茜岚, 汪金玉, 刘舒予, 占伊扬, 刘菁, 贾坚. 南京市鼓楼社区老年人群高脂血症与内皮细胞微粒的相关性[J]. 检验医学, 2023, 38(12): 1167-1172. |
| [11] | 代芳芳, 鲁辛辛, 于艳华, 陈铭, 孙桂珍. HIV/AIDS患者分枝杆菌检出情况分析[J]. 检验医学, 2023, 38(12): 1173-1176. |
| [12] | 顾玉, 梁晓艳, 马胜辉, 佟娜, 程明艳, 阎泽君. 血浆生物标志物在慢性肾脏病伴血栓栓塞患者中的表达及其近期预后评估价值[J]. 检验医学, 2023, 38(12): 1177-1182. |
| [13] | 周维, 诸佩超, 宋颖, 缪颖波, 赵强, 徐翀. 抗Xa因子活性室间质量评价调查品制备及应用[J]. 检验医学, 2023, 38(12): 1183-1185. |
| [14] | 努荣古丽·买买提, 衡燕, 张凯迪, 王新玲, 李慧, 杜丹阳, 董玲玲, 郭艳英. 乌鲁木齐地区成年男性骨代谢指标与代谢综合征的相关性分析[J]. 检验医学, 2023, 38(12): 1186-1190. |
| [15] | 李文静, 陆书华, 李晓哲, 戈宁宁, 董海新. 非O1/非O139群霍乱弧菌血流感染病原学和临床特征[J]. 检验医学, 2023, 38(12): 1191-1194. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||