
检验医学 ›› 2024, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (3): 227-236.DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8640.2024.03.004
景蓝汀1, 朱梦婷2, 杨振坤1, 罗园园1, 邹健1( ), 殷莹1(
), 殷莹1( )
)
收稿日期:2023-02-10
修回日期:2023-11-16
出版日期:2024-03-30
发布日期:2024-04-24
通讯作者:
殷 莹,E-mail:yyeffie@163.com;邹 健,E-mail:zoujan@njmu.edu.cn。
作者简介:景蓝汀,女,1996年生,硕士,主要从事临床检验工作。
JING Lanting1, ZHU Mengting2, YANG Zhenkun1, LUO Yuanyuan1, ZOU Jian1( ), YIN Ying1(
), YIN Ying1( )
)
Received:2023-02-10
Revised:2023-11-16
Online:2024-03-30
Published:2024-04-24
摘要:
目的 建立CD14反向辅助设门法(简称CD14反向法),并探讨其在淋巴细胞亚群检测中的应用。方法 在常规6色流式细胞术检测方案(常规法)中加入CD14-BV421抗体,建立CD14反向法。采用常规法和CD14反向法分别检测质控品、不同放置时间(4、24、48、72 h)的样本和不同疾病(系统性红斑狼疮、病毒性肺炎和肾移植术后)患者的淋巴细胞亚群,比较2种方法检测结果的差异和偏移情况。结果 CD14反向法检测细胞低值质控品的淋巴细胞百分比(LYMPH%)和自然杀伤(NK)细胞百分比(NK%)低于常规法(P<0.05);细胞中值质控品2种方法之间所有项目差异均无统计学意义(P>0.05)。与放置4 h比较,CD14+单核细胞与淋巴细胞的区分度随样本放置时间的延长而变小。与全血样本室温放置4 h比较,放置24 h后CD14反向法和常规法各项目的相对偏移均<5%,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05);放置48 h,CD14反向法各项指标相对偏移均<5%,常规法细胞毒性T淋巴细胞(CTL)(CD3+CD8+)、B细胞(CD3-CD19+)百分比及其绝对数的相对偏移均>5%;放置72 h,2种方法所有项目的相对偏移均>10%,为临床不可接受。采用CD14反向法检测系统性红斑狼疮、病毒性肺炎、肾移植术后患者外周血淋巴细胞亚群,可较好地区分淋巴细胞和单核细胞,同时减少非典型单核细胞对NK%和NK细胞绝对数的影响。结论 CD14反向法可减少流式细胞术检测中淋巴细胞门的误圈,有助于提高检测结果的准确性。
中图分类号:
景蓝汀, 朱梦婷, 杨振坤, 罗园园, 邹健, 殷莹. CD14反向辅助设门法在淋巴细胞亚群检测中的应用[J]. 检验医学, 2024, 39(3): 227-236.
JING Lanting, ZHU Mengting, YANG Zhenkun, LUO Yuanyuan, ZOU Jian, YIN Ying. Application of CD14 reverse assisted gate method in detection of lymphocyte subsets[J]. Laboratory Medicine, 2024, 39(3): 227-236.
| 方法 | LYMPH%/% | CD3+%/% | CD3+CD4+%/% | CD3+CD8+%/% | CD3-CD19+%/% | NK%/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CD14反向法 | 17.69±0.29 | 51.38±0.71 | 12.96±0.73 | 33.53±0.57 | 20.18±0.70 | 28.06±0.85① |
| 常规法 | 18.02±0.35** | 51.21±0.65 | 12.64±0.70 | 33.08±0.65 | 19.68±0.67 | 28.75±0.77①* |
| 靶值 | 54±9 | 14±7 | 36±6 | 21±5 | 21±4 | |
| 方法 | LYMPH#②/(个·μL-1) | CD3+细胞/(个·μL-1) | CD3+CD4+细胞/(个·μL-1) | CD3+CD8+细胞/(个·μL-1) | CD3-CD19+细胞/(个·μL-1) | NK细胞/ (个·μL-1) |
| CD14反向法 | 962.06±39.83 | 494.15±18.28 | 124.64±7.94 | 322.52±13.49 | 194.20±10.92 | 270.01±15.61① |
| 常规法 | 980.48±42.65 | 501.96±20.27 | 123.91±7.86 | 322.32±13.89 | 192.92±10.53 | 281.94±16.23① |
| 靶值 | 431±108 | 110±58 | 287±118 | 170±85 | 167±84 |
表1 不同方法检测细胞低值质控品结果比较
| 方法 | LYMPH%/% | CD3+%/% | CD3+CD4+%/% | CD3+CD8+%/% | CD3-CD19+%/% | NK%/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CD14反向法 | 17.69±0.29 | 51.38±0.71 | 12.96±0.73 | 33.53±0.57 | 20.18±0.70 | 28.06±0.85① |
| 常规法 | 18.02±0.35** | 51.21±0.65 | 12.64±0.70 | 33.08±0.65 | 19.68±0.67 | 28.75±0.77①* |
| 靶值 | 54±9 | 14±7 | 36±6 | 21±5 | 21±4 | |
| 方法 | LYMPH#②/(个·μL-1) | CD3+细胞/(个·μL-1) | CD3+CD4+细胞/(个·μL-1) | CD3+CD8+细胞/(个·μL-1) | CD3-CD19+细胞/(个·μL-1) | NK细胞/ (个·μL-1) |
| CD14反向法 | 962.06±39.83 | 494.15±18.28 | 124.64±7.94 | 322.52±13.49 | 194.20±10.92 | 270.01±15.61① |
| 常规法 | 980.48±42.65 | 501.96±20.27 | 123.91±7.86 | 322.32±13.89 | 192.92±10.53 | 281.94±16.23① |
| 靶值 | 431±108 | 110±58 | 287±118 | 170±85 | 167±84 |
| 方法 | LYMPH%/% | CD3+%/% | CD3+CD4+%/% | CD3+CD8+%/% | CD3-CD19+%/% | NK%/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CD14反向法 | 24.66±0.48 | 74.24±0.64 | 50.37±0.92 | 20.59±0.39 | 11.97±0.50 | 13.46±0.52 |
| 常规法 | 24.74±0.67 | 74.27±0.68 | 49.90±0.98 | 20.36±0.46 | 11.67±0.52 | 13.76±0.67 |
| 靶值 | 76±9 | 52±9 | 22±6 | 13±5 | 10±4 | |
| 方法 | LYMPH#/(个·μL-1) | CD3+细胞/ (个·μL-1) | CD3+CD4+细胞/(个·μL-1) | CD3+CD8+细胞/(个·μL-1) | CD3-CD19+细胞/(个·μL-1) | NK细胞/ (个·μL-1) |
| CD14反向法 | 1 249.29±30.33 | 927.54±28.14 | 629.38±23.15 | 257.24±8.01 | 149.51±5.98 | 168.06±6.19① |
| 常规法 | 1 253.47±36.96 | 931.08±31.96 | 625.60±23.67 | 255.15±9.16 | 146.21±6.25 | 172.38±9.02① |
| 靶值 | 836±260 | 598±165 | 255±118 | 141±67 | 110±56 |
表2 不同方法检测细胞中值质控品结果比较
| 方法 | LYMPH%/% | CD3+%/% | CD3+CD4+%/% | CD3+CD8+%/% | CD3-CD19+%/% | NK%/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CD14反向法 | 24.66±0.48 | 74.24±0.64 | 50.37±0.92 | 20.59±0.39 | 11.97±0.50 | 13.46±0.52 |
| 常规法 | 24.74±0.67 | 74.27±0.68 | 49.90±0.98 | 20.36±0.46 | 11.67±0.52 | 13.76±0.67 |
| 靶值 | 76±9 | 52±9 | 22±6 | 13±5 | 10±4 | |
| 方法 | LYMPH#/(个·μL-1) | CD3+细胞/ (个·μL-1) | CD3+CD4+细胞/(个·μL-1) | CD3+CD8+细胞/(个·μL-1) | CD3-CD19+细胞/(个·μL-1) | NK细胞/ (个·μL-1) |
| CD14反向法 | 1 249.29±30.33 | 927.54±28.14 | 629.38±23.15 | 257.24±8.01 | 149.51±5.98 | 168.06±6.19① |
| 常规法 | 1 253.47±36.96 | 931.08±31.96 | 625.60±23.67 | 255.15±9.16 | 146.21±6.25 | 172.38±9.02① |
| 靶值 | 836±260 | 598±165 | 255±118 | 141±67 | 110±56 |
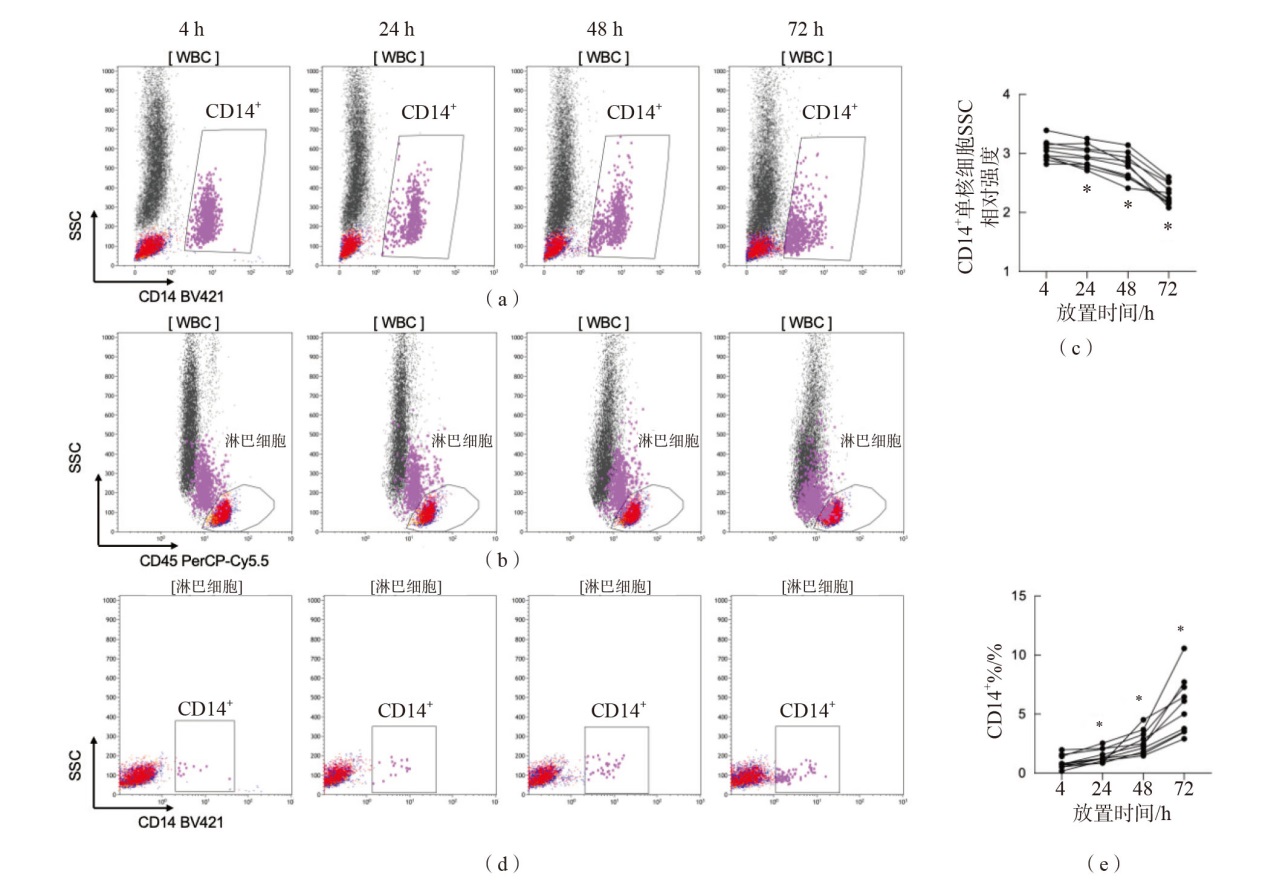
图4 样本放置不同时间CD14+单核细胞SSC相对强度的变化 注:(a)样本放置不同时间CD14+单核细胞的流式图;(b)样本放置不同时间淋巴细胞的流式图;(c)样本放置不同时间CD14+单核细胞SSC相对强度的变化;与放置4 h比较,*P<0.01;(d)样本放置不同时间淋巴细胞门内被误圈的CD14+单核细胞的流式图;(e)样本放置不同时间淋巴细胞门内被误圈的CD14+单核细胞的变化;与放置4 h比较,*P<0.01。
| 方法 | LYMPH% | CD3+% | CD3+CD4+% | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 检测值/% | 平均偏移①/% | 检测值/% | 平均偏移①/% | 检测值/% | 平均偏移①/% | |||||
| 放置4 h | ||||||||||
| 反向法 | 33.85(17.15,66.90) | 63.88(51.4,79.55) | 32.08(23.67,50.98) | |||||||
| 常规法 | 35.02(17.47,67.07) | 0.60 | 63.12(50.72,79.44) | -0.53 | 31.88(23.57,50.70) | -0.54 | ||||
| 放置24 h | ||||||||||
| 反向法 | 31.32(16.08,65.41) | -5.92 | 62.82(51.11,80.31) | 0.28 | 32.47(23.29,51.09) | -0.16 | ||||
| 常规法 | 31.85(16.50,66.15) | -4.59 | 62.25(50.09,79.77) | -0.93 | 32.05(23.21,50.68) | -1.40 | ||||
| 放置48 h | ||||||||||
| 反向法 | 31.62(15.81,61.55) | -7.64 | 65.22(50.89,81.10) | 1.81 | 31.17(23.8,50.40) | -0.48 | ||||
| 常规法 | 32.35(16.17,63.45) | -6.30 | 64.83(50.52,80.64) | 0.86 | 30.53(23.53,49.92) | -2.89 | ||||
| 放置72 h | ||||||||||
| 反向法 | 29.99(15.07,56.95) | -11.22 | 66.71(52.70,81.33) | 3.66 | 32.07(24.03,50.89) | 2.09 | ||||
| 常规法 | 31.92(15.66,60.18) | -6.78 | 65.63(52.73,81.36) | 3.32 | 31.43(23.86,50.37) | -0.46 | ||||
| 方法 | CD3+CD8+% | CD19+% | NK% | |||||||
| 检测值/% | 平均偏移①/% | 检测值/% | 平均偏移①/% | 检测值/% | 平均偏移①/% | |||||
| 放置4 h | ||||||||||
| 反向法 | 22.13(16.14,38.30) | 11.12(9.62,24.37) | 19.09(7.48,37.94) | |||||||
| 常规法 | 22.03(15.90,38.23) | -0.46 | 11.01(9.52,24.29) | -0.63 | 19.15(7.39,37.91) | 0.24 | ||||
| 放置24 h | ||||||||||
| 反向法 | 22.26(16.50,38.47) | 1.24 | 11.71(9.46,24.33) | 1.48 | 18.88(7.93,37.03) | -0.31 | ||||
| 常规法 | 22.06(16.19,38.20) | 0.01 | 11.55(9.22,24.04) | 0.12 | 19.02(7.91,36.88) | 0.26 | ||||
| 放置48 h | ||||||||||
| 反向法 | 23.31(16.55,41.07) | 4.93 | 11.28(8.41,23.16) | 4.94 | 18.79(6.93,37.51) | -2.95 | ||||
| 常规法 | 23.28(16.59,41.18) | 5.22 | 10.98(8.23,21.08) | -7.70 | 18.62(7.09,37.32) | -2.31 | ||||
| 放置72 h | ||||||||||
| 反向法 | 23.28(16.09,41.02) | 5.04 | 10.22(7.23,21.58) | -14.25 | 19.00(7.37,37.28) | -4.35 | ||||
| 常规法 | 23.44(16.34,41.10) | 6.39 | 9.91(7.03,21.50) | -15.24 | 18.62(7.46,36.54) | -5.06 | ||||
| 方法 | LYMPH# | CD3+细胞 | CD3+CD4+细胞 | |||||||
| 检测值/(个·μL-1) | 平均偏移①/% | 检测值/(个·μL-1) | 平均偏移①/% | 检测值/(个·μL-1) | 平均偏移①/% | |||||
| 放置4 h | ||||||||||
| 反向法 | 2 974.10(1 593.29,5 728.83) | 1 928.46(976.50,3 845.19) | 935.14(417.53,2 651.33) | |||||||
| 常规法 | 2 987.71(1 623.67,5 743.56) | 0.81 | 1 929.85(977.34,3 851.26) | -0.71 | 935.74(417.53,2 653.77) | -1.74 | ||||
| 放置24 h | ||||||||||
| 反向法 | 3 093.63(1 664.74,5 831.71) | 2.52 | 2 030.03(948.12,3 875.77) | 2.86 | 953.57(426.79,2 647.06) | 2.32 | ||||
| 常规法 | 3 126.31(1 707.74,5 876.17) | 3.97 | 1 925.12(949.91,3 871.79) | 1.86 | 954.75(427.94,2 648.57) | 1.40 | ||||
| 放置48 h | ||||||||||
| 反向法 | 3 021.64(1 614.04,5 307.23) | -0.34 | 1 928.68(960.37,3 684.93) | 1.42 | 908.26(446.15,2 525.46) | -0.96 | ||||
| 常规法 | 3 068.20(1 650.86,5 453.02) | 1.07 | 1 959.07(990.36,3 401.24) | 2.18 | 914.01(449.36,2 558.72) | -1.52 | ||||
| 放置72 h | ||||||||||
| 反向法 | 2 810.72(1 545.68,4 945.89) | -2.62 | 1 800.65(945.23,3 635.82) | 0.91 | 998.85(431.94,2 490.57) | -0.62 | ||||
| 常规法 | 2 867.21(1 599.00,5 204.78) | 1.67 | 1 854.35(1 037.68,3 811.74) | 4.96 | 1 017.09(435.10,2 542.77) | 1.12 | ||||
| 方法 | CD3+CD8+细胞 | CD19+细胞 | NK细胞 | |||||||
| 检测值/(个·μL-1) | 平均偏移①/% | 检测值/(个·μL-1) | 平均偏移①/% | 检测值/(个·μL-1) | 平均偏移①/% | |||||
| 放置4h | ||||||||||
| 反向法 | 618.28(363.50,1 133.36) | 336.99(154.84,1 397.66) | 535.29(267.28,1 247.97) | |||||||
| 常规法 | 619.29(363.90,1 135.18) | -0.66 | 337.20(154.84,1 396.34) | -0.79 | 551.00(268.51,1 270.33) | 0.45 | ||||
| 放置24 h | ||||||||||
| 反向法 | 645.91(364.74,1 150.39) | 3.89 | 360.11(157.61,1 419.14) | 3.92 | 550.74(246.06,1 284.01) | 1.43 | ||||
| 常规法 | 646.07(365.63,1 154.10) | 3.99 | 360.71(157.61,1 412.45) | 3.92 | 564.30(253.19,1 309.56) | 3.42 | ||||
| 放置48 h | ||||||||||
| 反向法 | 605.98(373.76,1 127.38) | 2.76 | 338.48(135.69,1 387.32) | -4.92 | 530.47(242.58,1 212.83) | -3.03 | ||||
| 常规法 | 607.83(385.11,1 157.51) | 5.72 | 346.86(135.89,1 309.75) | -5.29 | 552.27(248.10,1 233.32) | -0.79 | ||||
| 放置72 h | ||||||||||
| 反向法 | 564.77(346.79,1 113.08) | 2.41 | 284.49(111.78,802.21) | -16.47 | 461.42(238.60,1 089.22) | -6.91 | ||||
| 常规法 | 591.38(397.83,1 130.17) | 8.10 | 287.74(112.61,866.22) | -13.80 | 480.66(239.62,1 145.91) | -3.59 | ||||
表3 不同放置时间样本CD14反向法和常规法各项目的检测结果和偏移
| 方法 | LYMPH% | CD3+% | CD3+CD4+% | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 检测值/% | 平均偏移①/% | 检测值/% | 平均偏移①/% | 检测值/% | 平均偏移①/% | |||||
| 放置4 h | ||||||||||
| 反向法 | 33.85(17.15,66.90) | 63.88(51.4,79.55) | 32.08(23.67,50.98) | |||||||
| 常规法 | 35.02(17.47,67.07) | 0.60 | 63.12(50.72,79.44) | -0.53 | 31.88(23.57,50.70) | -0.54 | ||||
| 放置24 h | ||||||||||
| 反向法 | 31.32(16.08,65.41) | -5.92 | 62.82(51.11,80.31) | 0.28 | 32.47(23.29,51.09) | -0.16 | ||||
| 常规法 | 31.85(16.50,66.15) | -4.59 | 62.25(50.09,79.77) | -0.93 | 32.05(23.21,50.68) | -1.40 | ||||
| 放置48 h | ||||||||||
| 反向法 | 31.62(15.81,61.55) | -7.64 | 65.22(50.89,81.10) | 1.81 | 31.17(23.8,50.40) | -0.48 | ||||
| 常规法 | 32.35(16.17,63.45) | -6.30 | 64.83(50.52,80.64) | 0.86 | 30.53(23.53,49.92) | -2.89 | ||||
| 放置72 h | ||||||||||
| 反向法 | 29.99(15.07,56.95) | -11.22 | 66.71(52.70,81.33) | 3.66 | 32.07(24.03,50.89) | 2.09 | ||||
| 常规法 | 31.92(15.66,60.18) | -6.78 | 65.63(52.73,81.36) | 3.32 | 31.43(23.86,50.37) | -0.46 | ||||
| 方法 | CD3+CD8+% | CD19+% | NK% | |||||||
| 检测值/% | 平均偏移①/% | 检测值/% | 平均偏移①/% | 检测值/% | 平均偏移①/% | |||||
| 放置4 h | ||||||||||
| 反向法 | 22.13(16.14,38.30) | 11.12(9.62,24.37) | 19.09(7.48,37.94) | |||||||
| 常规法 | 22.03(15.90,38.23) | -0.46 | 11.01(9.52,24.29) | -0.63 | 19.15(7.39,37.91) | 0.24 | ||||
| 放置24 h | ||||||||||
| 反向法 | 22.26(16.50,38.47) | 1.24 | 11.71(9.46,24.33) | 1.48 | 18.88(7.93,37.03) | -0.31 | ||||
| 常规法 | 22.06(16.19,38.20) | 0.01 | 11.55(9.22,24.04) | 0.12 | 19.02(7.91,36.88) | 0.26 | ||||
| 放置48 h | ||||||||||
| 反向法 | 23.31(16.55,41.07) | 4.93 | 11.28(8.41,23.16) | 4.94 | 18.79(6.93,37.51) | -2.95 | ||||
| 常规法 | 23.28(16.59,41.18) | 5.22 | 10.98(8.23,21.08) | -7.70 | 18.62(7.09,37.32) | -2.31 | ||||
| 放置72 h | ||||||||||
| 反向法 | 23.28(16.09,41.02) | 5.04 | 10.22(7.23,21.58) | -14.25 | 19.00(7.37,37.28) | -4.35 | ||||
| 常规法 | 23.44(16.34,41.10) | 6.39 | 9.91(7.03,21.50) | -15.24 | 18.62(7.46,36.54) | -5.06 | ||||
| 方法 | LYMPH# | CD3+细胞 | CD3+CD4+细胞 | |||||||
| 检测值/(个·μL-1) | 平均偏移①/% | 检测值/(个·μL-1) | 平均偏移①/% | 检测值/(个·μL-1) | 平均偏移①/% | |||||
| 放置4 h | ||||||||||
| 反向法 | 2 974.10(1 593.29,5 728.83) | 1 928.46(976.50,3 845.19) | 935.14(417.53,2 651.33) | |||||||
| 常规法 | 2 987.71(1 623.67,5 743.56) | 0.81 | 1 929.85(977.34,3 851.26) | -0.71 | 935.74(417.53,2 653.77) | -1.74 | ||||
| 放置24 h | ||||||||||
| 反向法 | 3 093.63(1 664.74,5 831.71) | 2.52 | 2 030.03(948.12,3 875.77) | 2.86 | 953.57(426.79,2 647.06) | 2.32 | ||||
| 常规法 | 3 126.31(1 707.74,5 876.17) | 3.97 | 1 925.12(949.91,3 871.79) | 1.86 | 954.75(427.94,2 648.57) | 1.40 | ||||
| 放置48 h | ||||||||||
| 反向法 | 3 021.64(1 614.04,5 307.23) | -0.34 | 1 928.68(960.37,3 684.93) | 1.42 | 908.26(446.15,2 525.46) | -0.96 | ||||
| 常规法 | 3 068.20(1 650.86,5 453.02) | 1.07 | 1 959.07(990.36,3 401.24) | 2.18 | 914.01(449.36,2 558.72) | -1.52 | ||||
| 放置72 h | ||||||||||
| 反向法 | 2 810.72(1 545.68,4 945.89) | -2.62 | 1 800.65(945.23,3 635.82) | 0.91 | 998.85(431.94,2 490.57) | -0.62 | ||||
| 常规法 | 2 867.21(1 599.00,5 204.78) | 1.67 | 1 854.35(1 037.68,3 811.74) | 4.96 | 1 017.09(435.10,2 542.77) | 1.12 | ||||
| 方法 | CD3+CD8+细胞 | CD19+细胞 | NK细胞 | |||||||
| 检测值/(个·μL-1) | 平均偏移①/% | 检测值/(个·μL-1) | 平均偏移①/% | 检测值/(个·μL-1) | 平均偏移①/% | |||||
| 放置4h | ||||||||||
| 反向法 | 618.28(363.50,1 133.36) | 336.99(154.84,1 397.66) | 535.29(267.28,1 247.97) | |||||||
| 常规法 | 619.29(363.90,1 135.18) | -0.66 | 337.20(154.84,1 396.34) | -0.79 | 551.00(268.51,1 270.33) | 0.45 | ||||
| 放置24 h | ||||||||||
| 反向法 | 645.91(364.74,1 150.39) | 3.89 | 360.11(157.61,1 419.14) | 3.92 | 550.74(246.06,1 284.01) | 1.43 | ||||
| 常规法 | 646.07(365.63,1 154.10) | 3.99 | 360.71(157.61,1 412.45) | 3.92 | 564.30(253.19,1 309.56) | 3.42 | ||||
| 放置48 h | ||||||||||
| 反向法 | 605.98(373.76,1 127.38) | 2.76 | 338.48(135.69,1 387.32) | -4.92 | 530.47(242.58,1 212.83) | -3.03 | ||||
| 常规法 | 607.83(385.11,1 157.51) | 5.72 | 346.86(135.89,1 309.75) | -5.29 | 552.27(248.10,1 233.32) | -0.79 | ||||
| 放置72 h | ||||||||||
| 反向法 | 564.77(346.79,1 113.08) | 2.41 | 284.49(111.78,802.21) | -16.47 | 461.42(238.60,1 089.22) | -6.91 | ||||
| 常规法 | 591.38(397.83,1 130.17) | 8.10 | 287.74(112.61,866.22) | -13.80 | 480.66(239.62,1 145.91) | -3.59 | ||||
| 疾病 | 例数 | LYMPH#/% | CD3+/% | CD3+CD4+/% | CD3+CD8+/% | CD19+/% | NK细胞/% | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 系统性红斑狼疮 | 10 | 5.04±2.42 | -4.64±2.13 | -4.47±2.05 | -4.72±2.21 | -6.45±3.32 | 11.37(2.60,14.90) | ||
| 病毒性肺炎 | 30 | 5.04±2.42 | -2.81±1.88 | -2.82±1.89 | -2.85±1.89 | -2.91±1.86 | 4.39(0.40,6.76) | ||
| 肾移植术后 | 30 | 5.73±3.39 | -4.97±2.90 | -5.08±2.93 | -5.04±2.93 | -5.13±2.81 | 6.77(3.75,16.85) | ||
| 疾病 | LYMPH#/(个·μL-1) | CD3+细胞/(个·μL-1) | CD3+CD4+细胞/(个·μL-1) | CD3+CD8+细胞/(个·μL-1) | CD19+细胞/(个·μL-1) | NK细胞/ (个·μL-1) | |||
| 系统性红斑狼疮 | 5.04±2.42 | 0.06 (0.03,0.17) | 0.17 (0.06,0.38) | 0.00 (0.00,0.07) | 0.00 (-3.29,0.06) | 16.79 (7.13,19.45) | |||
| 病毒性肺炎 | 3.17±2.12 | 0.17 (0.08,0.32) | 0.15 (0.07,0.24) | 0.14 (0.00,0.32) | 0.00 (0.00,0.16) | 6.44 (2.88,11.14) | |||
| 肾移植术后 | 5.73±3.39 | 0.36 (0.23,0.46) | 0.22 (0.13,0.44) | 0.25 (0.14,0.37) | 0.00 (0.00,0.33) | 11.54 (8.37,27.40) | |||
表4 不同疾病患者CD14反向法与常规法检测结果的相对偏移
| 疾病 | 例数 | LYMPH#/% | CD3+/% | CD3+CD4+/% | CD3+CD8+/% | CD19+/% | NK细胞/% | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 系统性红斑狼疮 | 10 | 5.04±2.42 | -4.64±2.13 | -4.47±2.05 | -4.72±2.21 | -6.45±3.32 | 11.37(2.60,14.90) | ||
| 病毒性肺炎 | 30 | 5.04±2.42 | -2.81±1.88 | -2.82±1.89 | -2.85±1.89 | -2.91±1.86 | 4.39(0.40,6.76) | ||
| 肾移植术后 | 30 | 5.73±3.39 | -4.97±2.90 | -5.08±2.93 | -5.04±2.93 | -5.13±2.81 | 6.77(3.75,16.85) | ||
| 疾病 | LYMPH#/(个·μL-1) | CD3+细胞/(个·μL-1) | CD3+CD4+细胞/(个·μL-1) | CD3+CD8+细胞/(个·μL-1) | CD19+细胞/(个·μL-1) | NK细胞/ (个·μL-1) | |||
| 系统性红斑狼疮 | 5.04±2.42 | 0.06 (0.03,0.17) | 0.17 (0.06,0.38) | 0.00 (0.00,0.07) | 0.00 (-3.29,0.06) | 16.79 (7.13,19.45) | |||
| 病毒性肺炎 | 3.17±2.12 | 0.17 (0.08,0.32) | 0.15 (0.07,0.24) | 0.14 (0.00,0.32) | 0.00 (0.00,0.16) | 6.44 (2.88,11.14) | |||
| 肾移植术后 | 5.73±3.39 | 0.36 (0.23,0.46) | 0.22 (0.13,0.44) | 0.25 (0.14,0.37) | 0.00 (0.00,0.33) | 11.54 (8.37,27.40) | |||
| [1] | 盛慧明, 孙寒晓. 流式细胞术的发展与展望[J]. 中华检验医学杂志, 2018, 41(1):20-23. |
| [2] |
CHEN L, CHEN X, YAO W, et al. Dynamic distribution and clinical value of peripheral lymphocyte subsets in children with infectious mononucleosis[J]. Indian J Pediatr, 2021, 88(2):113-119.
DOI |
| [3] | 马锡慧, 高钰, 韩永, 等. 流式细胞术在肾移植术后感染中的诊断价值[J]. 器官移植, 2018, 9(2):137-141. |
| [4] | 段萃娟, 凌爱琴, 张翠, 等. 流式细胞仪检测外周血淋巴细胞亚群的常见问题及其解决方案[J]. 武警医学, 2021, 32(10):832-835. |
| [5] | 沈子园, 贺晨露, 王颖, 等. 淋巴细胞亚群检测在评估成人噬血细胞综合征预后中的价值[J]. 中华检验医学杂志, 2022, 45(9):914-920. |
| [6] |
SALEM D A, HENDAWY S R, NASSAR M K. Seroprevalence of Toxoplasma gondii among hemodialysis patients:a possible link to main T-lymphocyte subsets levels and dialysis adequacy[J]. Acta Trop, 2023, 237:106703.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
NARASIMHAN P B, MARCOVECCHIO P, HAMERS A A J, et al. Nonclassical monocytes in health and disease[J]. Annu Rev Immunol, 2019, 37:439-456.
DOI PMID |
| [8] | 姚林娟, 方卉, 何世波, 等. 异常样本状态对TBNK淋巴细胞亚群检测干扰与处理方法[J]. 中国卫生检验杂志, 2022, 32(11):1346-1349. |
| [9] | JERRAM A, GUY T V, BEUTLER L, et al. Effects of storage time and temperature on highly multiparametric flow analysis of peripheral blood samples;implications for clinical trial samples[J]. Biosci Rep, 2021, 41(2):BSR20203827. |
| [10] |
HOPE C M, HUYNH D, WONG Y Y, et al. Optimization of blood handling and peripheral blood mononuclear cell cryopreservation of low cell number samples[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2021, 22(17):9129.
DOI URL |
| [11] | HAUSER A, SCHRATTBAUER K, NAJDANOVIC D, et al. Optimized quantification of lymphocyte subsets by use of CD7 and CD33[J]. Cytometry A, 2013, 83(3):316-323. |
| [12] | CHERIAN S, LEVIN G, LO W Y, et al. Evaluation of an 8-color flow cytometric reference method for white blood cell differential enumeration[J]. Cytometry B Clin Cytom, 2010, 78(5):319-328. |
| [1] | 郑慧, 陈颖秀, 叶绿茵, 卢仁泉, 郭林. 结直肠癌患者外周血T淋巴细胞亚群与肿瘤进展的关系[J]. 检验医学, 2024, 39(4): 330-335. |
| [2] | 梁臻龙, 郭宇妮, 王楠, 王佳楠, 刘佳玉, 刘培培, 向代军, 王成彬, 李绵洋. 造血干细胞移植患者术后淋巴细胞亚群水平在移植物抗宿主病中的临床意义[J]. 检验医学, 2024, 39(4): 387-392. |
| [3] | 吴林军, 周翼, 蒲文杰, 刘于嵩. T淋巴细胞亚群和肝功能指标与慢性乙型肝炎患者中医辨证分型的相关性[J]. 检验医学, 2024, 39(2): 166-170. |
| [4] | 刘亚楠, 夏敏, 胡韶华, 郑月, 张泓. 淋巴细胞亚群、炎症因子和氨基末端B型钠尿肽原联合检测诊断川崎病[J]. 检验医学, 2023, 38(6): 532-537. |
| [5] | 刘俊闪, 郭明发, 孙佳, 史利欢, 刘炜, 段勇涛. 微量残留病监测在ETV6/RUNX1阴性和阳性急性B淋巴细胞白血病患儿预后中的意义[J]. 检验医学, 2023, 38(3): 209-214. |
| [6] | 张亚旭, 崔延伟, 刘紫烟. 核酸分子杂交-流式细胞术检测HPV E6/E7 mRNA初步研究[J]. 检验医学, 2023, 38(1): 46-50. |
| [7] | 谭美玉, 殳洁, 宣彬彬, 周丽达, 李红, 侯尚伟, 盛慧明. SARS-CoV-2疫苗接种对人体抗体产生和免疫功能的影响[J]. 检验医学, 2022, 37(8): 729-734. |
| [8] | 杜宇平, 陈阳. sCD147、sCD40L、miR-21与ACI患者颈动脉粥样斑块类型及预后的关系[J]. 检验医学, 2022, 37(7): 636-640. |
| [9] | 陶朝欣, 孙洁, 张玉娜, 白明明, 张校辉, 许丽亚, 邢江涛, 郝冀洪, 张牡霞. 血小板膜糖蛋白Ⅸ轻度缺乏巨大血小板综合征1例报道[J]. 检验医学, 2022, 37(7): 702-704. |
| [10] | 李华, 王伟亮, 谢贝, 杨瑜, 孟繁荣, 王楠, 刘志辉, 张言斌. 流式细胞术鉴定结核分枝杆菌利福平异质性耐药可行性分析[J]. 检验医学, 2022, 37(6): 577-582. |
| [11] | 刘训涛, 王霞, 赵飞, 郭迪媛, 张斌. 异常表达CD13的B细胞恶性肿瘤患者形态学和流式细胞术检测结果分析[J]. 检验医学, 2022, 37(5): 499-501. |
| [12] | 洪俊, 饶永彩. 基于CD157的四色法流式细胞术单核细胞和中性粒细胞PNH克隆检测方法的建立及评价[J]. 检验医学, 2022, 37(4): 377-381. |
| [13] | 苗林子, 陆遥, 屈晨雪, 由然, 龚岩. 健康成人白细胞表面CD64和HLA-DR相关指标参考区间的建立及其影响因素分析[J]. 检验医学, 2022, 37(3): 240-245. |
| [14] | 鞠颖慧, 莫惠芳, 吴蕙, 陈朴, 郭玮, 王蓓丽. 2种6色流式细胞术试剂检测淋巴细胞亚群的性能比较[J]. 检验医学, 2022, 37(3): 270-273. |
| [15] | 薛燕, 许俐, 党利亨, 王朝, 崔亚琼, 王萍, 王宁, 张新杰, 刘洋. 高浓度胆红素对流式细胞术外周血淋巴细胞亚群检测的干扰和消除方法[J]. 检验医学, 2022, 37(12): 1169-1173. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||