叶芸,女,1974年生,硕士,副主任技师,主要从事免疫学及分子生物学研究。
研究脑卒中患者血浆脂蛋白相关磷脂酶A2(Lp-PLA2)的变化,探讨其与缺血性脑卒中梗死灶大小和神经功能缺损程度的关系。
方法采用酶联免疫吸附试验(ELISA)测定180例缺血性脑卒中患者、165例出血性脑卒中患者及105名健康对照者(正常对照组)血浆Lp-PLA2水平,同时测定血脂[总胆固醇(TC)、甘油三酯(TG)、高密度脂蛋白胆固醇(HDL-C)、低密度脂蛋白胆固醇(LDL-C)]、葡萄糖(Glu)及纤维蛋白原(FIB)。采用受试者工作特征(ROC)曲线评价Lp-PLA2对缺血性脑卒中和出血性脑卒中的诊断效能;采用头颅核磁共振检查脑梗死体积大小,按照美国国立卫生研究所中风量表进行神经功能缺损程度评估;对缺血性脑卒中患者血浆Lp-PLA2与神经功能缺损程度评分进行相关性分析。
结果缺血性脑卒中组、出血性脑卒中组和正常对照组之间Lp-PLA2、TC、HDL-C、LDL-C、FIB水平差异均有统计学意义(
缺血性脑卒中患者血浆Lp-PLA2水平明显升高,与神经功能缺损程度评分密切相关。Lp-PLA2是缺血性脑卒中发病的独立危险因子,可成为缺血性脑卒中的预测指标和评价病情严重程度的重要指标。
To investigate the changes of lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2 (Lp-PLA2) level in patients with stroke, and to research the correlation with the volume of cerebral infarction and the severity of neurological impairment in patients with ischemic stroke.
MethodsA total of 180 ischemic stroke patients, 165 hemorrhagic stroke patients and 105 healthy subjects (healthy control group) were enrolled. By enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), the plasma Lp-PLA2 levels were determined, and the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve was used to evaluate the efficacy of Lp-PLA2 in the diagnosis of ischemic stroke and hemorrhagic stroke. The blood lipids [total cholesterol (TC), triglyceride (TG), high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C)], glucose (Glu) and fibrinogen (FIB) were determined. The volumes of cerebral infarction were measured by cranium magnetic resonance imaging,and the severities of neurological impairment were assessed by the National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale.The correlation of plasma Lp-PLA2 with the National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale was analyzed.
ResultsThe levels of Lp-PLA2, TC,HDL-C,LDL-C and FIB among ischemic stroke, hemorrhagic stroke and healthy control groups had statistical significance (
Plasma Lp-PLA2 increases significantly in patients with ischemic stroke, and it is significantly correlated with the National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale. Plasma Lp-PLA2 is an independent risk factor for ischemic stroke, and it may be a prediction index of ischemic stroke and a useful parameter for the severity of patient's condition.
脑卒中包括缺血性脑卒中和出血性脑卒中,是全球范围内流行最广的心脑血管疾病之一,死亡率占心脑血管疾病死亡的首位[
选取2009年1月至2011年12月在西安医学院附属医院住院的脑卒中患者345例,均为发病3 d之内的急性脑卒中患者。其中缺血性脑卒中180例,男110例,女70例,年龄48~65岁;出血性脑卒中165例,男100例,女65例,年龄45~68岁。缺血性脑卒中患者与出血性脑卒中患者的性别构成、年龄差异均无统计学意义( P>0.05)。对脑卒中患者按美国国立卫生研究所中风量表(NIHSS)进行神经功能缺损程度评分。脑梗死体积分型按Pullicino公式[核磁共振(MRI)扫描阳性层数÷2]计算,将其分为小梗死组(≤4 cm3)、中梗死组(>4~<10 cm3)、大梗死组(≥10 cm3)。脑卒中患者纳入标准:符合第4届全国脑血管病学术会议制定的脑卒中诊断标准[
1.主要试剂与仪器
人血浆脂蛋白相关磷脂酶 A2(Lp-PLA2)酶联免疫吸附试验(ELISA)试剂盒购自上海朗顿公司(美国进口)。血脂[总胆固醇(TC)、甘油三酯(TG)、高密度脂蛋白胆固醇(HDL-C)、低密度脂蛋白胆固醇(LDL-C)]及葡萄糖(Glu)检测采用日本奥林巴斯AU640全自动生化分析仪及原装配套试剂。FIB采用美国Beckman ACL-9000全自动血凝仪检测。
2. Lp-PLA2测定
采用ELISA双抗体夹心法测定Lp-PLA2水平。所有对象均于清晨空腹用乙二胺四乙酸(EDTA)抗凝管采集肘静脉血3 mL,混合10~20 min后在2~8 ℃下1 200× g离心20 min,分离上清液,置于Ep管。统一编号后置-80 ℃保存。
采用SPSS 11.5软件进行统计分析。各组年龄、体重指数等呈正态分布的连续变量均以 ±s表示,两样本比较采用两样本 t检验;多样本比较采用one-way ANOVA检验。TC、TG、HDL-C、LDL-C、Glu、FIB、Lp-PLA2呈偏态分布,用中位数(四分位数)表示,多组间比较用Kruskal-Wallis秩和检验判断各组间差异;然后采用Mann-Whitney U检验进一步做两两比较。性别非参数资料用Person χ2检验进行分析;Lp-PLA2与神经功能缺损程度评分之间的关系采用Spearman相关分析;诊断效能用受试者工作特征(ROC)曲线评价,总体诊断效能用ROC曲线下面积为(AUC)及95%可信区间( CI)表示。 P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
缺血性脑卒中组、出血性脑卒中组和正常对照组年龄、体重及性别构成差异均无统计学意义( F值分别为1.902、1.08, χ2=0.05, P均>0.05)。缺血性脑卒中组和出血性脑卒中组的NIHSS评分差异无统计学意义( t=-1.602, P>0.05);出血性脑卒中组中的高血压病例数明显多于缺血性脑卒中组( χ2=147.6, P<0.05)。
缺血性脑卒中组、出血性脑卒中组和正常对照组之间Lp-PLA2、TC、HDL-C、LDL-C、FIB水平差异均有统计学意义( P均<0.05);缺血性脑卒中组与出血性脑卒中组之间TG和Glu水平差异无统计学意义( P值分别为0.133、0.067),但与正常对照组比较差异有统计学意义( P均<0.05)。见表1:
| 表1 缺血性脑卒中组、出血性脑卒中组和正常对照组一般资料比较 |
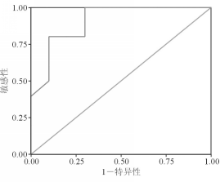
Lp-PLA2诊断缺血性脑卒中的AUC为0.905(95% CI:0.772~1.038),最佳临界值为42.35 μg/L,敏感性为81.5%,特异性为80.0%。见图1:
血浆Lp-PLA2 水平随脑梗死体积增加而呈递增趋势,但差异无统计学意义( P>0.05)。见表2:
| 表2 血浆Lp-PLA2 水平与脑梗死体积的关系 |
缺血性脑卒中的基本病因是动脉粥样硬化,近年来的研究表明动脉粥样硬化本质上是一种慢性炎症反应过程[
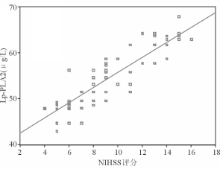
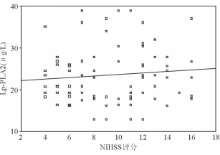
本研究结果显示缺血性脑卒中组、出血性脑卒中组和正常对照组之间血浆Lp-PLA2水平差异均有统计学意义( P均<0.05)。血浆Lp-PLA2水平随脑梗死体积增加呈递增趋势,但差异均无统计学意义( P>0.05)。提示血浆Lp-PLA2水平不能作为预测脑梗死体积大小的指标。Spearman相关分析表明,缺血性脑卒中患者血浆Lp-PLA2水平与神经功能缺损程度呈正相关( r=0.837, P<0.05),而出血性脑卒中患者血浆Lp-PLA2与神经功能缺损程度无相关性( r=0.276, P=0.127)。由此可见,Lp-PLA2可促进缺血性脑卒中的发生、发展且可作为病情严重程度的判定指标。同时,本研究结果还显示出血性脑卒中患者中高血压病例数明显多于缺血性脑卒中,进一步说明高血压是出血性脑卒中的重要发病因素。
国外有研究显示,循环中Lp-PLA2 的活性和水平升高与血管性事件的发生密切相关。Lp-PLA2作为1种炎症介质,可以独立预测缺血性心脑血管病的发生[
许多研究均发现缺血性脑卒中患者Lp-PLA2明显升高,本研究结果也进一步证实了这一点。Lp-PLA2对预测缺血性脑卒中发病风险、发展、预后有重要的临床价值,而且对临床早期诊断缺血性脑卒中有重要意义,可作为缺血性脑卒中的预测指标和评价病情严重程度以及治疗疗效观察的重要指标。
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|