低密度脂蛋白(low density lipoprotein,LDL)在密度、颗粒大小及化学组成等方面具有明显异质性。从颗粒大小方面分析,LDL主要分为两大类:一类颗粒较大、密度较小,称大而轻 LDL(large buoyant LDL,lbLDL);另一类颗粒较小、密度较大,称为小而密LDL(small dense LDL,sdLDL)。近年来,各种研究发现sdLDL与动脉粥样硬化的发生、发展密切相关。sdLDL与冠心病(coronary heart disease,CHD)的关系愈来愈受到人们的关注。目前sdLDL的主要检测方法有密度梯度超速离心法、梯度凝胶电泳法[ 1, 2],前者所用仪器昂贵、所需时间长,后者操作繁琐、分析速度慢。其他检测方法还有质子核磁共振光谱法[ 3]、体积排阻色谱法[ 4]、动态光散射法[ 5]以及微流控芯片电泳分离法[ 6]等,但都存在仪器复杂、操作繁琐等不足。我们通过筛选合适的沉淀剂并对沉淀条件进行优化,建立了更适用于常规实验室分离检测sdLDL的方法。
美国Beckman-Coulter公司Allegra 64R台式高速冷冻离心机,日立7600-020型全自动生化分析仪。
磷钨酸钠(批号F20070403)、氯化锰(MnCl2)(批号F20090224)购于国药集团化学试剂有限公司,氯化镁(MgCl2)(批号071115)、无水氯化钙(CaCl2)(批号071115)购于上海凌峰化学试剂有限公司,肝素钠(批号1012110)购于江苏万邦生化医药股份有限公司,硫酸葡聚糖钠盐(DSS)(批号HGC01)购于东京化成工业株式会社;血清总胆固醇(TC)、甘油三酯(TG)、高密度脂蛋白胆固醇(HDL-C)、低密度脂蛋白胆固醇(LDL-C)试剂由上海北海生物技术工程有限公司提供。
选择南通大学附属医院就诊患者,空腹安静状态下采集静脉血2 mL,1 h内分离血清作为待测样本。
将200 μL血清和200 μL沉淀剂依次加入离心管中混匀,37 ℃水浴10 min后冰浴15 min,然后于4 ℃,16 600 rpm离心15 min。此时,上清液中含sdLDL,下层沉淀含lbLDL、极低密度脂蛋白(VLDL)和乳糜微粒(CM)。使用全自动生化分析仪检测上清液中LDL-C含量即为血清中sdLDL-C含量。
1. 沉淀剂的筛选 分别用4种沉淀剂[ 7][磷钨酸-Ca2+(0.3%-15 mmol/L);硫酸葡聚糖(DS)-Mg2+(1.5%-40 mmol/L);肝素-Mn2+(40 U/mL-30 mmol/L);肝素-Mg2+(150 U/mL-90 mmol/L)]处理1组血脂正常血清和2组血脂升高血清。使用全自动生化分析仪测定上清液中TC、TG、 HDL-C和LDL-C,考察沉淀效果。
2. 沉淀剂浓度的选择 选择合适的沉淀剂,考察不同浓度沉淀剂的沉淀效果。
3. 精密度检测 将sdLDL-C浓度为0.47和0.99 mmol/L的混合血清用化学沉淀法分别连续检测20次,计算批内CV;将sdLDL-C浓度为0.31和0.82 mmol/L的混合血清用化学沉淀法分别连续检测20 d,计算批间CV。.
4. 线性试验 将sdLDL-C高值血清样本(浓度为1.44 mmol/L)用生理盐水作梯度稀释,使含血清分别为1/10、2/10、3/10、4/10、5/10、6/10、7/10、8/10、9/10及原血清,用化学沉淀法测定sdLDL-C浓度,分析其线性范围。
5. 回收率 取sdLDL-C浓度为0.210 mmol/L的血清20 μL,加入180 μL sdLDL-C浓度为0.297 mmol/L的血清。用化学沉淀法测定样本中sdLDL-C浓度,计算回收率。
应用SPSS17.0统计软件进行统计学分析。计量资料以±s表示,组间比较采用单因素方差分析。P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
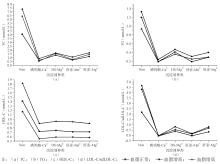
1. 最佳沉淀剂 分别用磷钨酸-Ca2+(0.3%-15 mmol/L)、DS-Mg2+(1.5%-40 mmol/L)、肝素-Mn2+(40 U/mL-30 mmol/L)和肝素-Mg2+(150 U/mL-90 mmol/L)处理1组血脂正常血清和2组血脂升高血清,4种沉淀剂沉淀效果见图1:
肝素-Mg2+(150 U/mL-90 mmol/L)作为沉淀剂时效果最好,2组血脂升高组sdLDL-C浓度分别是正常组的2.42和2.02倍。
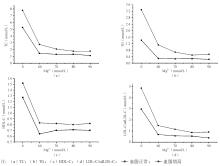
2. 最优沉淀剂浓度 沉淀剂中肝素浓度初定为150 U/mL,Mg2+浓度在40~90 mmol/L范围内10 mmol/L递进,处理血脂正常和血脂升高2组血清,测定上清液中TC、TG、 HDL-C和LDL-C,沉淀效果见图2:
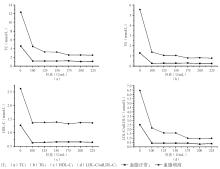
Mg2+浓度为40、50 mmol/L时无法沉淀脂蛋白;90 mmol/L时沉淀效果最好,血脂升高组sdLDL-C浓度是正常组的2.40倍。沉淀剂中Mg2+浓度为90 mmol/L,肝素浓度在25~225 U/mL范围内以25 U/mL递进,处理血脂正常和血脂升高2组血清,测定上清液中TC、TG、 HDL-C和LDL-C,沉淀效果见图3:
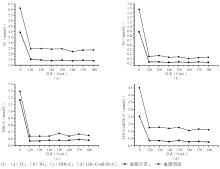
肝素浓度为25、50、75 U/mL时无法沉淀脂蛋白;150 U/mL时沉淀效果最好,血脂升高组sdLDL-C浓度是正常组的3.79倍。由于上述试验中肝素浓度在150~175 U/mL时上清液中sdLDL-C浓度变化幅度较大。为优化沉淀条件,再次调整肝素浓度,选择肝素浓度在120~180 U/mL范围内以10 U/mL递进,沉淀效果见图4:
肝素浓度为140 U/mL时沉淀效果最好,血脂升高组sdLDL-C浓度是正常组的2.17倍。因此,最终选择140 U/mL肝素-90 mmol/L Mg2+作为沉淀剂。
本法测定血清sdLDL-C的批内CV分别为2.83%、3.19%,批间CV分别为5.49%、6.13%。
本法测定sdLDL-C在0.14~1.44 mmol/L范围内线性关系良好,线性回归方程为Y=1.025X-0.197,r=0.988。
本法测定sdLDL-C的回收率为83.81%。
近年来,众多学者研究发现,sdLDL 在动脉粥样硬化的发生、发展过程中起重要作用,是冠心病的危险因子[ 8]。如何建立快速、简便的sdLDL检测方法也成为国内外许多专家学者研究的热点。但目前sdLDL的检测方法多由于需要特殊仪器设备或操作过程繁琐等不足难以在临床常规实验室推广使用。国外有关sdLDL化学沉淀法已有报道[ 9, 10],国内虽有采用化学沉淀法测定sdLDL的报道[ 11, 12],但大多直接引用国外方法。
本研究根据聚阴离子与二价阳离子组合可选择性沉淀密度<1.044 g/mL的脂蛋白,比较了4种沉淀剂的沉淀效果。结果发现140 U/mL肝素-90 mmol/L Mg2+作为沉淀剂较使用其他3种沉淀剂或其他浓度肝素-Mg2+能更有效地区分血脂升高组与正常组的sdLDL-C浓度。因此,最终选择140 U/mL肝素-90 mmol/L Mg2+作为沉淀剂。
本研究显示化学沉淀法测定sdLDL-C批内、批间重复性均较好,且此法在检测范围内具有良好的线性关系,样本回收率为83.81%。由于实验条件有限,本研究尚未将化学沉淀法与密度梯度超速离心法比较,但Hirano等[ 7]已证实化学沉淀法与密度梯度超速离心法有很好的相关性(Y=1.049X+1,r=0.884,P<0.000 1)。Hirano等[ 7]使用150 U/mL肝素-90 mmol/L Mg2+作为沉淀剂,与本研究所述化学沉淀法在肝素浓度上存在差异,可能与实验具体条件差异以及血清样本来源的种族差异有关。
与密度梯度超速离心法、梯度凝胶电泳法等比较,化学沉淀法具有不需特殊仪器设备、样本用量少、操作简便、成本低廉等优点,更适合常规实验室检测血清sdLDL-C含量。化学沉淀法的研究与应用将有力推动sdLDL临床价值的研究。
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|